CYBER SECURITY CONSULTING SERVICE AWARDS AND RECOGNITIONS
CyberSecOp's comprehensive managed security services, cyber security consulting, professional services, and data protection technology are recognized as industry-leading threat detection and response solutions by major analyst firms, key media outlets, and others.
How to Improve Data Security & Data Privacy
What are the biggest challenges currently facing data security and privacy?
As organizations embark on digital transformation, there is a clear need for enterprise data privacy and protection. New data privacy laws and the growing enforcement of existing regulations challenge organizations. And most organizations face rapid data growth and proliferation across the enterprise. Organizations have more data, more use cases, and more locations than ever before
First what is data privacy?
Data privacy and data protection are very closely interconnected, so much so that users often think of them as synonymous. But the distinctions between data privacy vs. data protection are fundamental to understanding how one complements the other. Privacy concerns arise wherever personally identifiable information is collected, stored, or used.
Second what is data security?
Data security is about securing data against unauthorized access. Data privacy is about authorized access — who has it and who defines it. Another way to look at it is this: data protection is essentially a technical issue, whereas data privacy is a legal one.
Data encryption ensure only privilege users has access
Data encryption isn't just for the technical advanced; modern tools make it possible for anyone to encrypt emails and other information. "Encryption used to be the sole province of geeks and mathematicians, but a lot has changed in recent years. In particular, various publicly available tools have taken the rocket science out of encrypting (and decrypting) email and files. based on what your need are our firm can help you implement the right technologies to ensure data security.
Stronger Password and Multi-factor Authentication
Password and Multi-Factor are essential when protecting data and data privacy from unauthorized users, or attackers. unfortunately many user don’t understand the importance of passwords. So much so that the 20 most commonly used passwords not only contain highly insecure passwords like the word “password”, they also account for a whopping 10.3% of all passwords that are being used. CyberSecOp recommend creating passwords that contain a minimum of 8 characters. If your password protects something sensitive, like access to your bank account, then use a minimum of 12 characters. all password should contain at lease one upper and lower case, and a symbol. don’t use the same passwords for every site, you can use difference variations of the password making it easier to recall. Example: Chase Bank : Iwanttolive1o8chase% Facebook:Iw@nttoliv3fb.
Enable two-factor authentication.
On top of having good passwords, consider enabling two-factor authentication when you sign into your email, bank website or any other sensitive account. When using two-factor authentication, a code will be sent to your phone when you sign in. You then input the code to access your account. Hackers likely don’t have access to your phone, so this can be a great way to add a layer of password security and data security. It may feel like additional work, but the extra protection can go a long way.
All organization needs an Ethical Hacker team like CyberSecOp
An ethical hacker is one who mimics the actions of a malicious hacker so as to detect security risks in advance and thus prevent breaches and attacks.
Any organization or business can hire the services of an ethical hacker to test/monitor the organization’s defenses, perform IT health checks and penetration tests, to assess the security of the systems and to evaluate the overall security of the organization’s network. An ethical hacker can provide valuable help to an organization by detecting vulnerabilities in a system/network on time and thus prevent the exploitation of data (customer data, financial data and other sensitive data), which could happen as a result of cybercriminals exploiting the vulnerabilities.
Backup is an essential part of data security
Backups are most often overlooked, data protection and backing up your data is essential when you have a major security event such has ransomware. Basically, this creates a duplicate copy of your data so that if a device is lost, stolen, or compromised, you don't also lose your important information. It's best to create a backup on a different device, such as an external hard drive, so that you can easily recover your information when the original device becomes compromised. It is critical that once the backup has complete to physically disconnect the backup device for the system, if the backup drive stay connected and your system becomes affect by ransomware, your backup data could also be affected.
Data Security, Data Privacy & Compliance
CyberSecOp can provide guidance and assistance with addressing privacy and data security practices, as well as to ensure that the practices and program implemented are compliant with relevant laws and regulations. The EU and some US Federal agencies, including the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) and the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), have been promulgating updated guidelines and recommendations for privacy and data security best practices in a variety of industries, including some of the newer Internet of Things and peer platform (sharing economy) marketplaces. Additionally, several industry groups have adopted self-regulatory programs and rules, including certification programs, to which a company can voluntarily abide.
In view of these guidelines and others, companies are further encouraged to establish internal policies and procedures to ensure compliance. Business policies may include a top-level information security and privacy policy, which expresses a commitment to data security and privacy from the top-level officers of a company, a risk management program, an acceptable use policy, access compartmentalization, communications monitoring, breach reporting, a document retention policy and outsourcing policies. Technical policies may include a variety of commitments to technical controls to ensure the protection of data, including encryption, passwords, authentication protocols, disaster recover, intrusion detection, physical security, patching and the like.
Cloud Security - Cloud Cyber Security
Cloud Security - Cloud Cyber Security
Of the large amount of data that has been moved to the cloud, a huge segment of it has been compromised. The compromised data includes election data, financial information like bank cards, health data, etc. Maintaining integrity and security continues to be a significant challenge for cloud platforms. [3]
In an attempt to provide extra security for cloud data, many cloud service providers (CSPs), have launched extensive cloud security technologies. Google has announced ‘shielded VMs’ to prevent hostile attacks. Even with these security technologies in place, however, users still have a large role to play in keeping their data safe.
In many cases, IT teams have recognized the lack of control when data is placed in the cloud. This lack of control is a symptom of the absence of an overarching security strategy. The challenge presents itself when an organization transfers data to the CSPs without maintaining any additional backup, as this could result In the loss of data at times. Stressing on the importance to maintain an additional backup of data. [3]
Another common challenge with the cloud is the unclear point-to-point access. Access permissions are complicated when an organization’s data is placed on a third-party cloud server. Planning and strategizing the access controls around crucial data is as important as defining the access points and control measures. Security in the cloud is different from on-premises security, making it complex due to the various rules implemented and security issues faced, such as failure to encrypt data. Access to the cloud server should be defined on a point-to-point basis. That means that access to data should be restricted based on the requirement of every individual, whether management or staff, should be clearly defined. A flow chart explaining the access points should be shared with the CSP to bring them on equal understanding to avoid conflicts.
Securing Your Data on the Cloud
The main objective of cloud security is to keep data secure, sharing the responsibility between the provider and the client. Here are some good practices that can be implemented to leverage the benefits of cloud services.
a) Encryption of Data
End-to-end encryption of data in transit
For high-security processes, where the data is highly confidential, all interactions with servers should happen over a secure socket layer (SSL) transmission. To ensure the end-to-end encryption of data, the SSL should terminate within the CSP’s network. Comprehensive encryption, when performed at the file level, makes cloud security stronger. All data should be encrypted before being uploaded to the cloud.
Encryption of data when at rest
Even when data is at rest, encryption should be enabled. This helps in complying with regulatory requirements, privacy policies, and contractual obligations related to confidential data. Before registering with your CSP, security policies should be verified with an auditor. AES-256 is used for encrypting data in the cloud and the keys should be encrypted with master keys in the rotation. Field-level encryption will also help keep the data secure.
b) Robust and Continuous Vulnerability Testing and Incident Response
A good CSP contract includes regular vulnerability assessment and incident response tools that extend to devices and networks. The solutions given by incidence response tools might enable automated security assessments to test system weaknesses. CSPs should be able to perform scans on demand.
c) End-user Device Security
Securing cloud-connected end-user devices is an often-overlooked component of a well-rounded security program. When utilizing infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS) or platform-as-a-service (PaaS) models, deploying firewall solutions in your end devices to protect the network perimeter is very important.
d) A Private Cloud and Network are Best
Opting for a cloud environment which is private and where you can have complete control over access to your data is the preferred method as opposed to using a multi-tenant instance. Also, opt for cloud storage or software-as-a-service (SaaS) which belongs to only you and is not shared with others. These personal clouds are called virtual private clouds (VPC) and all traffic to and from these VPCs can be routed to the corporate data center. This can be done through an internet protocol security (IPsec) hardware VPN connection.
e) Compliance Certifications
The two most important certifications that you should consider are SOC 2 Type II and PCI DSS.
SOC 2 Type II is a type of regulatory report that defines the internal controls of how a company should safeguard its customer data and operation controls. SOC2 deals with regulatory compliance, internal risk management processes, and vendor management programs. It confirms that a cloud service has robust management as it is specifically designed to ensure higher standards of data security.
PCI DSS – PCI DSS stands for Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard and is important to organizations that deal with credit card transactions. Meeting this standard helps keep cardholder data safe from fraud. It ensures that sensitive data stored in a cloud is processed and transmitted in a secure manner. It impacts security policies, procedures, software design, network architecture, and various protective measures.
Leading public cloud providers like Microsoft and Amazon offer proprietary credential management tools to provide legitimate access and keep intruders away from sensitive data. Having sophisticated tools can help ensure the security of your data in the cloud.
Defense is a matter of strict design principles and security policies scattered over various departments. By implementing the above key guidelines as part of your cloud strategy, you are on your way to securing your data in the cloud.
Ethical Hacker for Secure Cloud Storage
An ethical hacker is a skilled trained professional who knows how to locate the vulnerabilities in target systems, including cloud storage platforms and networks. The term ‘ethical’ differentiates a black-hat hacker from a white-hat hacker.
5 steps for preventing ransomware
5 steps for preventing ransomware
Hardening Your Environment Against Ransomware
To avoid ransomware infection, follow these steps:
1. Back up your computers and servers regularly.
Regularly back up the files on both the client computers and servers. Either back up the files when the computers are offline or use a system that networked computers and servers cannot write to. If you do not have dedicated backup software, you can also copy the important files to removable media. Then eject and unplug the removable media; do not leave the removable media plugged in.
2. Lock down mapped network drives by securing them with a password and access control restrictions.
Use read-only access for files on network drives, unless it is absolutely necessary to have write access for these files. Restricting user permissions limits which files the threats can encrypt.
3. Deploy and enable the following Endpoint Protection:
Implement and managed endpoint antivirus on all endpoint to prevent ransomware, most ransomware can be detected by popular antivirus.
4. IPS/IDS
IPS blocks some threats that traditional virus definitions alone cannot stop. IPS is the best defense against drive-by downloads, which occurs when software is unintentionally downloaded from the Internet. Attackers often use exploit kits to deliver a web-based attack like CryptoLocker through a drive-by download.
See Enabling network intrusion prevention or browser intrusion prevention.
5. Download the latest patches for web application frameworks, web browsers, and web browser plug-ins.
Attacking exploit kits cannot deliver drive-by downloads unless there is an old version of a plug-in to exploit, such as Flash. Historically, attacks were delivered through phishing and web browsers. Recently, more attacks are delivered through vulnerable web applications, such as JBOSS, WordPress, and Joomla.
6. Use an email security product to handle email safely.
CryptoLocker is often spread through spam emails that contain malicious attachments. Scanning inbound emails for threats with a dedicated mail security product or service is critical to keep ransomware and other malware out of your organization. For important advice and recommendations, see:
How to remove ransomware
There is no ransomware removal tool or CryptoLocker removal tool. Instead, if your client computers do get infected with ransomware and your data is encrypted, follow these steps:
1. Do not pay the ransom.
If you pay the ransom:
· There is no guarantee that the attacker will supply a method to unlock your computer or decrypt your files.
· The attacker uses the ransom money to fund additional attacks against other users.
2. Isolate the infected computer before the ransomware can attack network drives to which it has access.
3. Update the virus definitions and scan the client computers.
New definitions are likely to detect and remediate the ransomware. Configure Endpoint Protection to automatically downloads virus definitions to the client, as long as the client is managed and connected to the Symantec Endpoint Protection Manager.
4. Restore damaged files from a known good backup.
No security Endpoint Protection cannot decrypt the files that ransom lockers have sabotaged.
Submit the malware to antivirus provider.
If you can identify the malicious email or executable, submit it to antivirus provider.
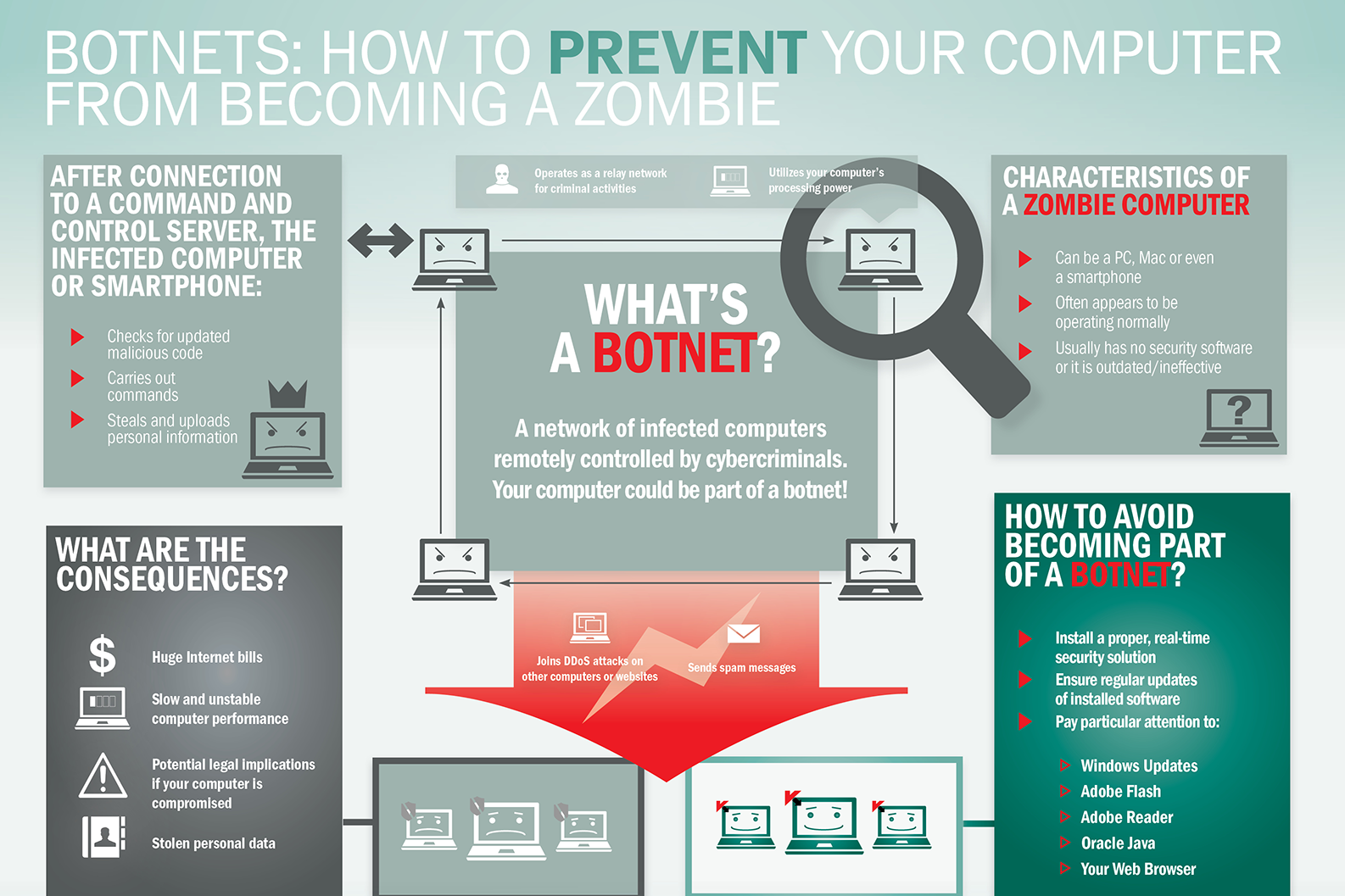
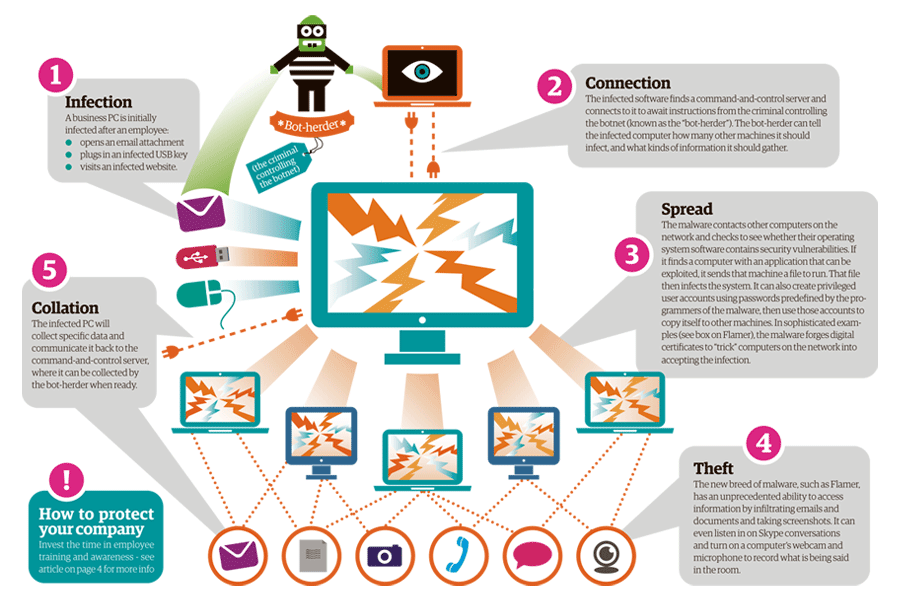
What is Botnet - Cybercriminals #1 Weapon
The word Botnet is formed from the words ‘robot’ and ‘network’. Cybercriminals use special Trojan viruses to breach the security of several users’ computers, take control of each computer and organise all of the infected machines into a network of ‘bots’ that the criminal can remotely manage.
Botnet Prevention- What is Botnet
How Botnets can impact you
Often, the cybercriminal will seek to infect and control thousands, tens of thousands or even millions of computers – so that the cybercriminal can act as the master of a large ‘zombie network’ – or ‘bot-network’ – that is capable of delivering a Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attack, a large-scale spam campaign or other types of cyberattack.
In some cases, cybercriminals will establish a large network of zombie machines and then sell access to the zombie network to other criminals – either on a rental basis or as an outright sale. Spammers may rent or buy a network in order to operate a large-scale spam campaign.
How to prevent your computer becoming part of a Botnet
Installing effective anti-malware software will help to protect your computer against Trojans and other threats.
Secure Google Chrome from Hacking Attacks
Google Chrome is definitely one of the most popular web browsers being used today. Hackers, as we know, are perpetually after whatever gets popular in the world of the internet. This because whatever is popular would help them target more people and steal more data. Thus, Google Chrome too happens to be among the most favorite for cyber criminals across the world. Hence, securing Google Chrome against hacking attacks is really important.
So, how do we secure Google Chrome from cyber attacks? Well, it’s a multi-step process. Lots of things have to be done. Securing your browser is important as it helps secure your device, your internet connection and more importantly, your personal and business data.
Let’s discuss, in detail, what all needs to be done to secure Google Chrome from hacking attacks. Here we go:
Begin by ensuring that your Google account is properly secured!
This is something basic, your Google account needs to be properly secured. Chrome lets you sign in from any device, anytime. Hence, it’s important to ensure the security of your Google account. You need to make sure you are logged out of your account every time you sign in, on any device. You also need to ensure that your password is secure. If you aren’t signed out or if someone knows/cracks your password, it would be easy to manipulate things and cause you harm. Your data could be stolen.
Keeping the browser secured is equally important…
Keeping the browser secured is as important as securing your Google account. You could use a password to protect your browser, and thus, in your absence, no one would be able to take control of your browser and do mischiefs. Similarly, every time you leave your terminal, it’s good to go out of the browser as well.
Keep your browser ‘clean’!
You should make it a habit to keep your browser ‘clean’, by wiping out most of the information from it. In fact, there should be some plan/schedule as regards cleaning the browser. Clear the history periodically, either everytime you log out or at least once every week if not once a day.
Never save passwords on the browser
The browser might offer to ‘remember’ your passwords for you so that you could sign in easily the next time you’re using some service. But it’s always good not to save passwords on the browser. If you save your passwords, it would be possible for someone else to get into your account and misuse it or steal information.
Having a master password helps
Having a master password, which would help you get to your other saved passwords in Chrome, is a good thing to do. Thus you need not worry about remembering all of your passwords and you don’t have to be afraid of your passwords getting stolen or misused either.
Keep your device protected
The device that you use to browse needs to be protected from malware and hacking. For this, you must use whatever security tools you need and also have alerts that tell you if at all your device is compromised. Remember a compromised device means an unsecured browser!
Keep the device locked whenever you’re not using it
Always keep your device locked when you are not using it, be it a computer or any other mobile device. That prevents people from getting on to your device and hijacking your browser and your data as well. Locking your device also gets it off the WiFi network that you are using.
Secure your network, never use unsafe WiFi networks
Securing your network is important; it helps a lot in securing Google Chrome from hacking attacks. Hence you need to do all that is needed to secure your network. Similarly, it’s always advisable never to use unsafe WiFi networks. Whenever you’re using a WiFi network, ensure it’s properly encrypted and if possible use an app or program that would prevent hacking. In fact, using a secure network secures not just your browser, but everything on your device/system.
Trust Chrome for phishing detection
Google Chrome does its own phishing detection and protects you from many phishing websites. So, when your browser tells you that a website is not safe, it’s always advisable to trust it and avoid such sites.
Avoid phishing websites and attachments yourself
In addition to Google Chrome detecting phishing websites for you, it’s always good that you yourself stay away from websites/attachments that could be used for phishing scams. Staying away from such suspicious websites secures your browser, your system/network and your data.
Cyber-Digital Task Force
The Department of Justice’s internal “Cyber-Digital Task Force,” created by Attorney General Jeff Sessions in February, will release its first-ever public report later this month at the Aspen Institute’s annual Security Forum, a department spokesperson told CyberScoop.
The report is expected to detail a series of security recommendations that the government should consider to protect future U.S. elections from a myriad of different threats, including foreign hacking attempts.
A statement by the DOJ previously explained that the Task Force will “prioritize its study of efforts to interfere with our elections; efforts to interfere with our critical infrastructure; the use of the Internet to spread violent ideologies and to recruit followers; the mass theft of corporate, governmental, and private information; the use of technology to avoid or frustrate law enforcement; and the mass exploitation of computers and other digital devices to attack American citizens and businesses.”
When Sessions launched the group earlier this year, he requested that an initial report be completed by June 30. The recommendations were submitted ahead of time, according to DOJ spokesperson Ian Prior. The answers are currently being reviewed ahead of publication.
The DOJ’s disclosure was made hours after the Democratic National Committee (DNC) issued a press release criticizing the department and Trump administration for missing various cybersecurity policy deadlines, including the June 30 submission. The agency contends that it in fact made the deadline, although the publication won’t occur for a few weeks. The Aspen Security Forum begins on July 18.
The creation of the Cybersecurity Task Force on Feb. 20 came less than a week after Special Counsel Robert Mueller indicted a group of Russian internet trolls for interfering in U.S. politics. The Russians allegedly ran an extensive social media campaign that worked to trick American voters in the run-up to the 2016 presidential election, the indictment claims.
Deputy Attorney General Rod Rosenstein is expected to make “an exclusive policy announcement” on July 19 at the Aspen Institute event.